All types of circuit breakers are important materials for any type of electrical installation, but to ensure their operation, you must understand the ideal type of circuit breaker for each need. It is a fundamental part of all constructions to ensure safety. So let’s know a little more about them.
What are they for:
The circuit breakers are installed inside a distribution board, where all the wiring responsible for conducting electricity is located. It is one of the most important parts of electrical installations, as it defines the electrical load that each wire must receive, with the help of devices responsible for this protection, such as circuit breakers.
There are several types of circuit breakers and they are very useful and essential devices in an electrical installation, their mechanism serves to interrupt the circuit, if it identifies an electrical current greater than it can withstand, it disarms. It is very important and easily found in the installations, they are usually installed in the energy meter and in the distribution boards, to protect their respective circuits.
Types of circuit breakers:
There are three basic varieties of circuit breakers: standard circuit breakers (which include single-pole and two-pole circuit breakers), ground-fault interrupting circuit breakers (GFCIs), and arc-fault interrupting circuit breakers (AFCIs).
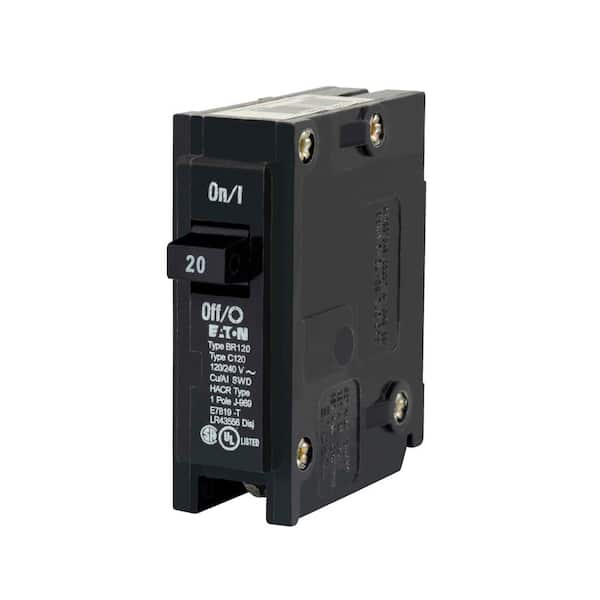
Single-Pole Circuit Breakers:
Single-pole circuit breakers are the type most often found in homes today. They’re named single-pole because they’re designed to monitor the current of a single wire and trip in the event of a short or electrical overload. Single-pole breakers are intended to accommodate between 15 and 30 amps and deliver 120 volts to the circuit.
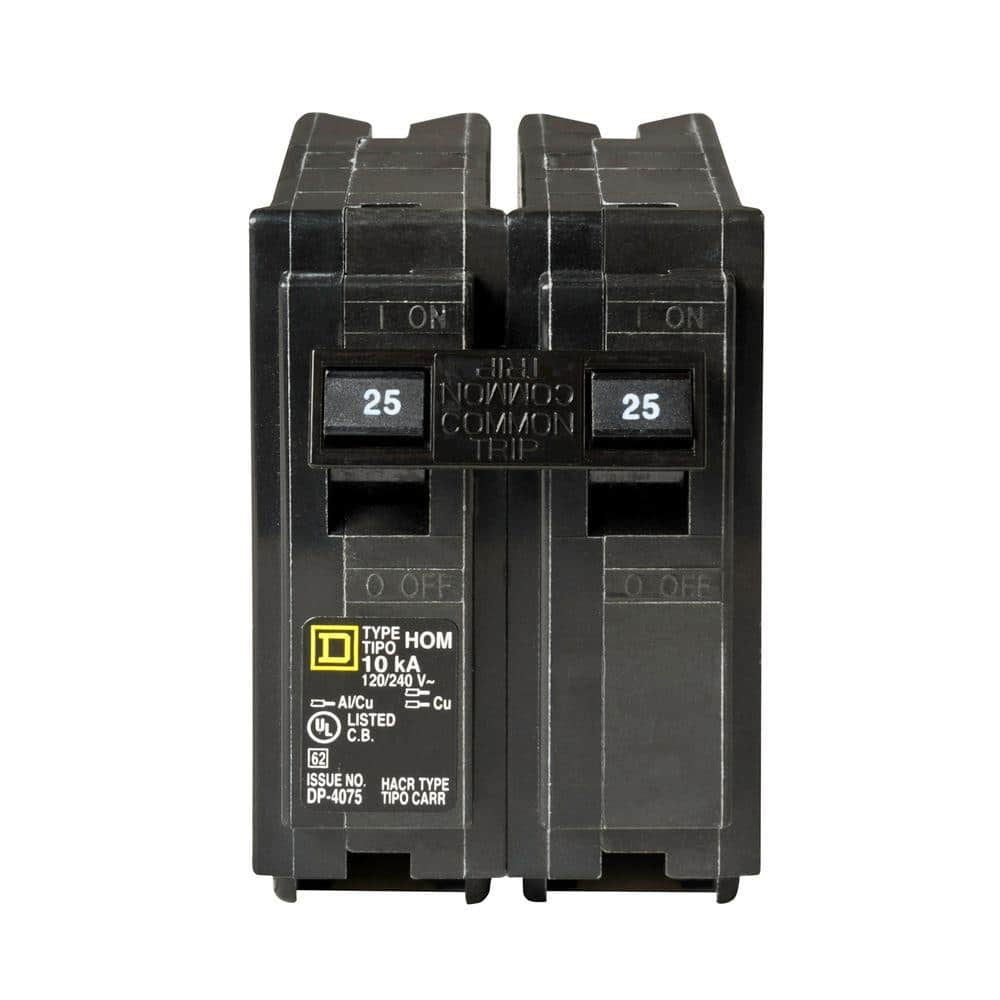


Double-Pole Circuit Breakers:
Double-pole circuit breakers monitor the flow of electricity through two wires simultaneously. They’re easily recognized as a single breaker with two interlinked, side-by-side switches. This type of breaker will trip if one or both of the wires short out or becomes overloaded. Double-pole circuit breakers deliver either 240 volts or 120/240 volts to an electrical circuit and can accommodate anywhere from 15 amps to 200 amps. Circuits that supply power to appliances that require a substantial amount of energy, such as washing machines and dryers, demand double-pole breakers.
GFCI Circuit Breakers:
GFCI circuit breakers are designed to protect against a line-to-ground fault. This is when a dangerous electrical path occurs between a grounded element and an electrical current. GFCI breakers also offer protection against an electrical short or overloaded current. These breakers are required by some electrical codes for areas in the home that can become wet such as bathrooms, laundry rooms and outdoor areas.


AFCI Circuit Breakers:
AFCI circuit breakers are designed to trip when arcing is detected within electrical wiring. This occurs when an electrical cord becomes damaged or its coating becomes too thin and presents a serious fire risk. Standard single-pole and double-pole circuit breakers won’t always detect electrical arcs because they’re only tripped by excessive heat. AFCI circuit breakers are required as part of the electrical code on newer houses.